The European Union Agency for Cybersecurity releases today the 2019 Annual Report on Trust Services Security Incidents.
For the year 2019, 27 EU countries and 2 EFTA countries reported 32 security incidents that had a significant impact on trust services in the EU. The 2019 Annual Report published today gives an aggregated overview of these security breaches showing root causes, statistics and trends. This report marks the fourth round of security incident reporting for the EU’s trust services sector.
According to the EU regulation on Electronic Identification and Trust Services (eIDAS), trust service providers must notify security breaches to their national supervisory body. The national supervisory bodies send annual summary reports about these breaches to ENISA and to the European Commission. ENISA aggregates this information in its Annual Reports.
Key takeways from the 2019 incident report:
- A significant increase in notified incidents: with an increase of nearly 80% in terms of reported incidents compared to the previous year.
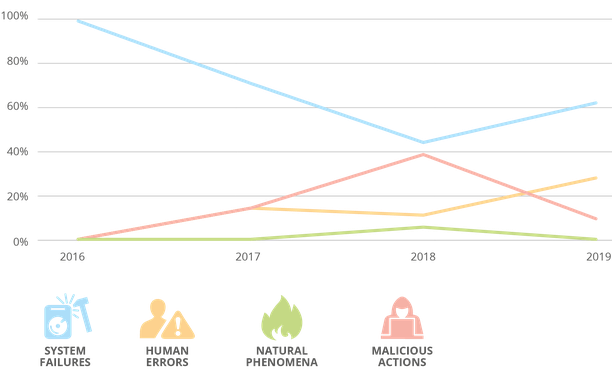
- System failures as the dominant root cause: they account for more than 60% of the incidents and remain the dominant root cause over the past four years of incident reporting.
- Most reported incidents concerned qualified trust services: more than three quarters of total incidents (78 %) had an impact on qualified trust services.
- Most of the incidents were minor: most incidents were minor, but a third of the incidents (31%) were rated as having a large impact. Unlike the previous two years, in 2019 there were no reports about incidents with impact rated as disastrous.
General observations:
- Supervision of, and incident reporting by, non-qualified services: statistics of the reported incidents suggest there is under-reporting of security breaches with non-qualified trust services.
- Reporting about vulnerabilities and attacks-in-the-wild: there is a clear need to exchange information not only about actual incidents with impact at a TSP’s trust service, but also about attacks and vulnerabilities.
To access the report, please visit: Trust Services Security Incidents 2019 Annual Analysis Report
ENISA and the eIDAS regulation
The Agency will continue to support the national supervisory bodies to implement the breach reporting under the Article 19 of the eIDAS regulation, and will work towards making this process efficient, effective and yielding statistics. Such data are useful for the supervising bodies, for the authorities of other sectors, as well as for the trust service providers and the organisations relying on these trust services.
In this direction, ENISA has recently released a new Visual Tool - CIRAS designed to increase transparency about cybersecurity incidents. The online visual tool, accessible to the public, gives now access to 4 years of trust services incident reports and to 8 years of telecom security incidents, aggregating as many as 1100 cybersecurity incidents. The new visual tool also allows for analysis of multiannual trends.
Background information
Electronic trust services include a range of electronic services around digital signatures, digital certificates, electronic seals, timestamps, etc. used to secure electronic, online, transactions.
The eIDAS regulation is the EU wide legal framework meant to ensure the interoperability and security of the electronic trust services across the EU. One of the goals of the eIDAS is to ensure electronic transactions can have the same legal validity as traditional paper - based transactions, to create a framework in which a digital signature has the same value has a hand-written signature.
This regulation is important for the European digital market because it allows businesses and citizens to work and use digital services across the EU. Adopted in July 2014, the eIDAS regulation came into force in 2016.
Security is an important pillar of the overall framework. Article 19 of the eIDAS regulation requires trust service providers in the EU to assess risks, take appropriate security measures, mitigate security breaches. They notify breaches to the national supervisory bodies who, in turn send annual summary reports about the notified breaches to ENISA and the Commission. ENISA publishes aggregated data on a yearly basis.
Security and trust are crucial factors in making eIDAS a success. ENISA supports the European Commission and the EU Member States with implementing the security requirements of the eIDAS regulation and supports collaboration and exchange of information between national supervisory bodies in Europe about the security of trust services.
Further information
ENISA webisite - Incident Reporting Topic
For questions related to the press and interviews, please contact press (at) enisa.europa.eu.

